Mood Disorder Treatment
Mood disorders affect nearly one in ten U.S. adults each year. According to the National Comorbidity Survey Replication, about 9.7% of the adult population experiences a mood disorder annually, with a higher prevalence among females (11.6%) compared to males (7.7%).
Throughout their lives, approximately 21.4% of U.S. adults will encounter some form of mood disorder. These conditions encompass a range of disorders, including depression and bipolar disorder, that can deeply impact a person’s quality of life.
Our center provides comprehensive and personalized treatment for mood disorders. Our approach is rooted in a deep understanding of these disorders’ physiological, psychological, and social dimensions, ensuring that each patient receives the tailored care necessary to manage and overcome their condition.

What is a Mood Disorder?

A mood disorder is a mental health condition characterized by significant alterations in a person’s emotional state that severely impact their daily functioning. These disorders, which include major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and several others, are not just occasional feelings of sadness or mood swings. They are profound and persistent emotional states that can dramatically affect a person’s thinking, behavior, and overall quality of life.
Without effective management, mood disorders can lead to a wide range of emotional, behavioral, and physical health issues, complicating tasks and relationships at home and work. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are crucial, as these conditions can lead to debilitating disruptions in the lives of those affected and their families.
Types of Mood Disorders
Mood disorders may be characterized by prolonged disturbances in mood that significantly impede daily functioning. Here’s an overview of the common types:
Major Depressive Disorder (Depression)
Depression is marked by persistent sadness and a lack of interest in activities once enjoyed, alongside other emotional and physical problems. It disrupts a person’s ability to function effectively daily. For a diagnosis, symptoms of depression must be present for at least two weeks.
Bipolar Disorder
This disorder is known for extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). These affect sleep, energy levels, behavior, judgment, and the ability to think clearly.
- Bipolar I disorder: Involves periods of severe mood episodes from mania to depression.
- Bipolar II disorder: A milder form of mood elevation involving milder episodes of hypomania that alternate with periods of severe depression.
- Cyclothymic disorder: A chronically unstable mood state with hypomania and mild depression episodes lasting for at least two years.
Dysthymia (Persistent Depressive Disorder)
Characterized by a long-lasting depressed mood that lasts for two years or more, dysthymia is less severe than major depression but more chronic. It involves symptoms that aren’t as strong as major depression but still cause significant impairment.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
A form of depression is influenced by seasonal changes, typically worsening during the fall and winter months when there is less sunlight. Treatment often involves light therapy, psychotherapy, and medications.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
A severe form of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), PMDD causes extreme mood shifts that can disrupt work and damage relationships. Symptoms usually start seven to ten days before menstruation and end shortly after its onset.
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD)
This condition is typically diagnosed in children and involves severe irritability, anger, and frequent, intense temper outbursts that are disproportionate to the situation.
Depression with Psychotic Features
A severe form of depression where the individual experiences psychosis. This may include delusions or hallucinations, often with themes of depression like personal inadequacy or guilt.
Each type of mood disorder has unique symptoms and treatment approaches. Recognizing and treating mood disorders early can significantly improve the quality of life and functionality of those affected.
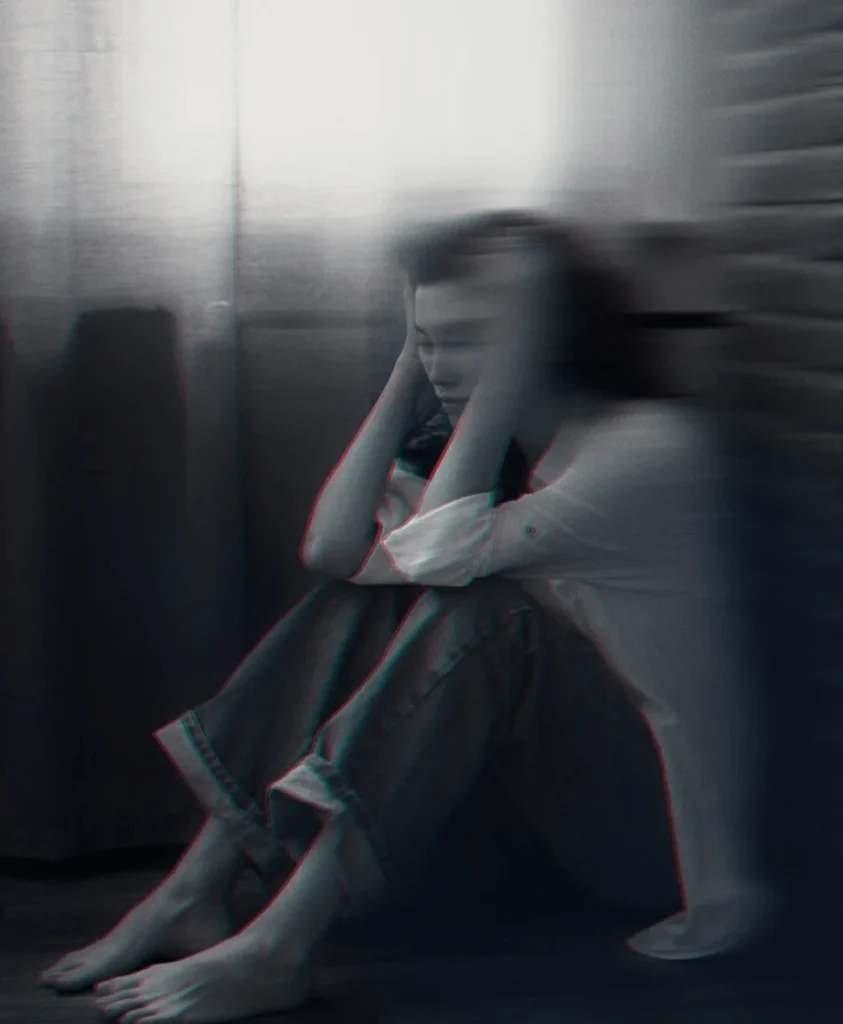

Signs and Symptoms of Mood Disorders
Our center provides comprehensive and personalized treatment for mood disorders. Our approach is rooted in a deep understanding of these disorders’ physiological, psychological, and social dimensions, ensuring that each patient receives the tailored care necessary to manage and overcome their condition.
Mood disorders manifest through a spectrum of symptoms that significantly impact emotional well-being and functionality. These symptoms include:
- Persistent sadness or irritability: Continual feelings of sadness or irritability that linger and affect daily life.
- Extreme emotional shifts: Experiencing severe mood swings, from elevated manic states to deep depressive episodes, often disrupting normal functioning.
- Social withdrawal: A noticeable loss of interest in social activities and hobbies that were previously enjoyed, leading to isolation.
- Changes in appetite and sleep patterns: Drastic changes such as significant weight gain or loss, insomnia, or hypersomnia, which disrupt normal routines.
These symptoms often result in considerable distress and may coincide with other serious conditions such as anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and postpartum depression.

What Causes Mood Disorders?
Mood disorders are complex conditions influenced by genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Here’s how these elements interplay:
Biological Factors
The brain’s structure plays a crucial role, especially in areas like the amygdala and the orbitofrontal cortex, which regulate emotions. Imaging studies often reveal an enlarged amygdala in individuals with mood disorders, indicating a biological underpinning that affects emotional processing.

Genetic Influences
A significant familial predisposition exists for mood disorders. Individuals with a family history of such conditions are at a higher risk, suggesting a strong genetic component that may predispose them to develop similar issues.

Environmental Triggers
Life experiences significantly impact mood disorders. Stressful life events such as the loss of a loved one, ongoing stress, traumatic incidents, and early childhood abuse are potent triggers. Moreover, chronic physical illnesses like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and heart disease have also been linked to the development of mood disorders, particularly depression.
Understanding these factors is crucial in effectively recognizing, diagnosing, and treating mood disorders. Each component plays a part in the onset and progression of these complex conditions.
Who is at Risk for Mood Disorders?
Mood disorders can affect anyone, but certain factors significantly increase the risk. Here’s a closer look at who is most vulnerable:
Genetic Predisposition
A strong family history of mood disorders such as depression or bipolar disorder substantially raises the risk. If a close relative has experienced these conditions, their siblings, children, or extended family members are also more likely to develop similar mood disorders.


Stressful Life Changes
Significant life stressors, such as job loss, divorce, financial troubles, or the death of a loved one, can trigger or exacerbate mood disorders. These intense or prolonged stressors can lead to persistent sadness or depression, making them difficult to manage without professional help.
Gender-Specific Risk
Statistically, women are nearly twice as likely to be diagnosed with depression compared to men. This increased risk may be related to hormonal fluctuations, societal pressures, or both.


Comorbid Conditions
Individuals dealing with other mental health issues like anxiety disorders or those undergoing significant life changes, such as postpartum women, are at an elevated risk. Additionally, certain medications and medical conditions can induce or worsen mood disorders, making careful diagnosis and treatment essential.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early identification and management of mood disorders, potentially mitigating their impact through timely intervention.
How Are Mood Disorders Diagnosed?
Diagnosing mood disorders involves a comprehensive approach that integrates clinical assessments with detailed medical and psychological evaluations.
At our center, mental health professionals begin with a thorough interview that covers the patient’s psychiatric history, symptom profile, and any relevant family history of mood disorders. Physical examinations and lab tests often supplement this to rule out other medical conditions that could mimic or contribute to mood symptoms.
Diagnosis is guided by criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which helps clinicians differentiate between various types of mood disorders, such as major depression, bipolar disorder, and others, based on specific symptom clusters and duration.
How Are Mood Disorders Treated?
Diagnosis is guided by criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which helps clinicians differentiate between various types of mood disorders, such as major depression, bipolar disorder, and others, based on specific symptom clusters and duration.
Psychiatric Evaluation
We begin with a thorough psychiatric assessment to accurately diagnose the type of mood disorder, considering factors like symptom patterns, family history, and previous treatment responses.
Medication Management
Our treatment team, including expert psychiatrists, carefully evaluates the need for medications such as antidepressants and mood stabilizers. We ensure that any pharmaceutical approach is carefully tailored to minimize side effects and maximize efficacy.
Psychotherapy
A cornerstone of our treatment, psychotherapy, particularly Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), is utilized to address negative thought patterns and emotional disturbances associated with mood disorders. This treatment helps individuals understand and change their thoughts and behaviors, improving their mood and reducing disorder symptoms.
Lifestyle Counseling
We emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications in managing mood disorders. Our team guides diet, exercise, and sleep habits to enhance physical health and emotional well-being.
Support Groups
Patients have the opportunity to join support groups where they can connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and strategies in a supportive environment can be incredibly beneficial in managing symptoms and preventing relapse.
Advanced Therapeutic Techniques
For those who require more intensive interventions, we offer additional therapies such as Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) for emotional regulation and Mindfulness-Based Interventions to help manage difficult emotions more effectively.
Family Therapy and Support
Recognizing the vital role of family, we include family therapy and support as crucial components of our treatment programs. This helps improve the patient’s overall support system, enhancing recovery outcomes.
Educational Workshops and Psychoeducation
Our programs are complemented by educational sessions that help patients and their families understand the nature of mood disorders and the importance of ongoing management strategies.

Get Help with Mood Disorder Treatment Today
Supporting someone with a mood disorder can significantly affect their recovery and quality of life. Here are some strategies to consider:

- Educate yourself: Learn about the specific mood disorder to better understand the challenges and behaviors associated with the condition.
- Be patient and understanding: Recognize that recovery is an ongoing process and symptoms fluctuate.
- Offer emotional support: Listen actively and offer reassurance. Sometimes, just being there is more helpful than trying to fix their issues.
- Encourage consistent treatment: Support their efforts to attend therapy sessions and adhere to their treatment regimen.
- Help establish a routine: Assist them in creating a daily schedule that includes time for treatment, relaxation, and social activities.
- Monitor warning signs: Help them recognize early signs of mood swings or depression and encourage them to discuss these with their healthcare provider.
Get Help with Mood Disorder Treatment Today
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a mood disorder, reaching out for help is crucial. Contact us today to learn more about our specialized mood disorder treatment programs to support and rejuvenate your emotional health.
At Twilight Recovery Center, we are committed to helping you regain control over your life and return to the path of wellness. Remember, seeking help is a proactive step towards recovery and managing your mood disorder effectively.


